Choosing the components of a package can be a major undertaking. The purpose of this technical library is to provide our customers with an overview of some of the common themes and terminology that might be encountered in creating a packaging solution. Please feel free to direct further questions to our experienced sales staff and allow them to assist you in working through the details of creating the perfect package for your marketing needs.
Bottle Finish Terminology
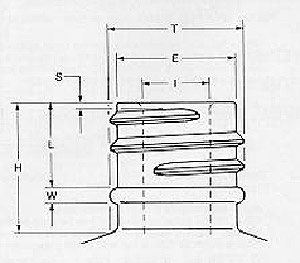
A finish is the configuration of the top of the container shaped to accommodate a specific closure. The first number refers to the cap in diameter (in millimeters). The second number refers to the height and thread configuration of a closure or finish.
- S: Thread Start– Distance from top of finish to top of the start of the thread.
- L: Bead Locating Dimension – Distance from top of finish to top of bead.
- H: Finish Height – Distance from top of finish to the intersection of the projected “T” diameter and the shoulder slope (except for 400 with bead)
- T: Major Diameter – Measurement across the threads.
- E: Minor Diameter – Root diameter of thread.
- W: Bead Width
- I: Hole Diameter
Common Neck Finishes
Standard Snap Fit
Standard Recess Snap Fit
Standard Friction
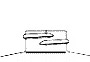
Standard 400
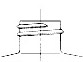
Standard 410
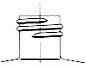
Standard 415
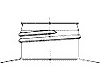
Pour Lip
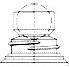
Roll On
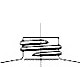
Standard 425

Cello-Seal Bead
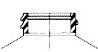
General Purpose
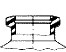
Serum Finish
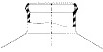
Snap Finish
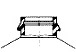
Bellows Snap Finish
Glossary of Terms
Amber
A yellowish-brown color of glass or plastic containers used primarily to protect light-sensitive contents.
Autoclavable
A method used to sterilize containers with superheated steam under pressure.
Bail
The curved handle of a pail.
Blowmolding
A process used for forming hollow containers in which the plastic is placed inside a mold and forced outward via air pressure to assume the shape of that mold cavity.
Capacity
The volume of space inside a container that holds a given amount of product.
Closed-head drum
A container that has the TOP and BOTTOM ends seamed to the body. (Also known as a tight-head drum.)
Closure
A metal or plastic cap which effects a primary seal when properly applied to the container.
Cork finish
The bottle opening (finish) that is sealed with a cork.
C-T closure
A continuous-thread design that begins near the bottom of the closure skirt and continues upward toward the liner. Closure size designation determines number of turns.
C-T finish
A continuous-thread finish that features an uninterrupted protruding helix on the neck of a container to accommodate a screw-type closure.
Density
Weight per unit volume of a substance, expressed in grams per cubic centimeter, pounds per cubic foot and so on.
Dispensing closure
A closure designed to be used to apply the contents of a container.
Dome
A closure that has a rounded surface.
Drop test
A test of strength accomplished by dropping an object in a specified manner for a specified number of times, or until the article fails from impact.
Dropper cap
A bottle closure that features a dropper or rubber bulb designed to dispense liquids.
Ears
Parts smoldered, dumped, or riveted to the side of a can or pail to which a bail (or handle) is inserted for easier carrying.
Extrusion
The shaping of a plastic material by forcing it through a specially shaped die.
F style can
A rectangular base can fitted with a screw cap.
Finish
The portion of the neck of a container designed to accommodate a particular closure.
Fitment
A device used as part of a closure assembly designed to accomplish a specific purpose, such as a powder shaker, sprinkler or dropper.
Fittings
Any parts (other than ends) necessary to complete the closure of a can, including plugs, screw necks, spouts, bungs, caps, etc.
Flame treating
A method of exposing plastics to an open flame to increase the polarity of the surface, rendering it more receptive to inks, lacquers, paints, adhesives, etc.
Flowed-in-gasket
A gasket formed by a liquid material (vinyl or latex), poured (or flowered) directly into a gasket groove, and cured in place, usually by baking; i.e. plastisol.
Gasket
A liner applied between adjoining parts to make a tight seal.
Injection blowmolding
A two-stage, plastic bottle manufacturing process. First, a preform (or parison) is injection molded, forming the bottle finish. Then, the preform is transferred to a blow mold where the bottle takes its ultimate shape.
Largeware
A term given to containers that are over one gallon in capacity.
Linerless closure
A closure that has been engineered to function in specific applications without the use of a liner.
Lug pail cover
A type of cover usually used on open-end pails or drums. The pail cover is lined with a “cushiony” compound that seats on the top rim of the pail. The seal is “activated” by clinching the lugs (an integral part of the cover) to the pail rim.
Multilayer bottles
Containers composed of layers of specially selected plastics which are coextruded so that the unique characteristics of each material are retained. The objective is to improve the barrier qualities of the container, which can result in a longer shelf life.
Narrow mouth
The finish of a container that is small in proportion to the diameter of the body.
Natural color
Describes the translucent appearance of a plastic material which has not been colored.
Neck
The part of the container where the bottle cross-section slenderizes to form the finish.
Orifice
An opening in a dispensing closure or fitment from which the product is dispensed.
Overcap
A closure (usually plastic) provided with some cans. It is used to cover the open end once the can has been opened. Sometimes it is used to describe a closure which is used for covering the primary closure or other dispensing system, such as a fingertip sprayer or aerosol valve.
Phenolic
The generic name for phenol-formaldehyde thermosetting plastic that is molded or cast.
Polyethylene, high-density (HDPE)
In the high-density grade, this thermoplastic material is more rigid and less permeable than the low density grade. It also displays a higher tolerance to distortion temperatures.
Polyethylene, low-density (LDPE)
Squeezability is good, especially in the low-density grade of this thermoplastic material. It also displays better resistance to impact than the high-density grade.
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
A resin with outstanding clarity and good resistance to impact, along with good barrier properties to resist grease and oil, cold and sunlight.
Polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG)
A resin with good barrier properties and outstanding clarity, with a slightly higher tolerance to distortion temperatures as compared to PET.
Polypropylene (PP)
A tough, lightweight, rigid plastic made by the polymerization of propylene in the presence of an organometallic catalyst at relatively low pressures and temperatures.
Polystyrene (PS)
Thermoplastic compound used to make plastic containers, closures, etc.
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
A thermoplaxtic material composed of polymers of vinyl chloride; a colorless solid with outstanding resistance to water, alcohols, concentrated acids, and alkalis.
Shelf life (or storage life)
The length of time a product can be stored under specified temperature conditions and still remain usable.
Tamper-evident
Any device which shows visible signs that the container has been opened.
Thread
The profile of a container finish which will accommodate specific closures.
Universal Product Code (UPC)
A 10 digit, all-numeric code which uniquely identifies products.
Unlined
A closure with no liner.
Urea
The generic name for urea-formaldehyde—-the thermosetting compound that is used to mold light-colored closures.
Widemouth
Containers with a large finish opening, or those that have a large finish size in proportion to their capacity.
Window stripe
A see-through vertical stripe on a molded container; used primarily to monitor the level of the contents.
Liner Chart (PDF – 113KB)